Analyzes pattern causality matrices to compute and summarize the directional effects of different causality types (positive, negative, dark) between system components.
Value
An object of class "pc_effect" containing:
positive: Data frame of positive causality effects
negative: Data frame of negative causality effects
dark: Data frame of dark causality effects
items: Vector of component names
summary: Summary statistics for each causality type
Details
Calculate Pattern Causality Effect Analysis
The function performs these key steps:
Processes raw causality matrices
Computes received and exerted influence for each component
Calculates net causality effect (difference between received and exerted)
Normalizes results to percentage scale
Related Packages
vars: Vector autoregression for multivariate time series
lmtest: Testing linear regression models
causality: Causality testing and modeling
See also
pcMatrix for generating causality matrices
plot.pc_effect for visualizing causality effects
Examples
# \donttest{
data(climate_indices)
dataset <- climate_indices[, -1]
pcmatrix <- pcMatrix(dataset, E = 3, tau = 1,
metric = "euclidean", h = 1,
weighted = TRUE)
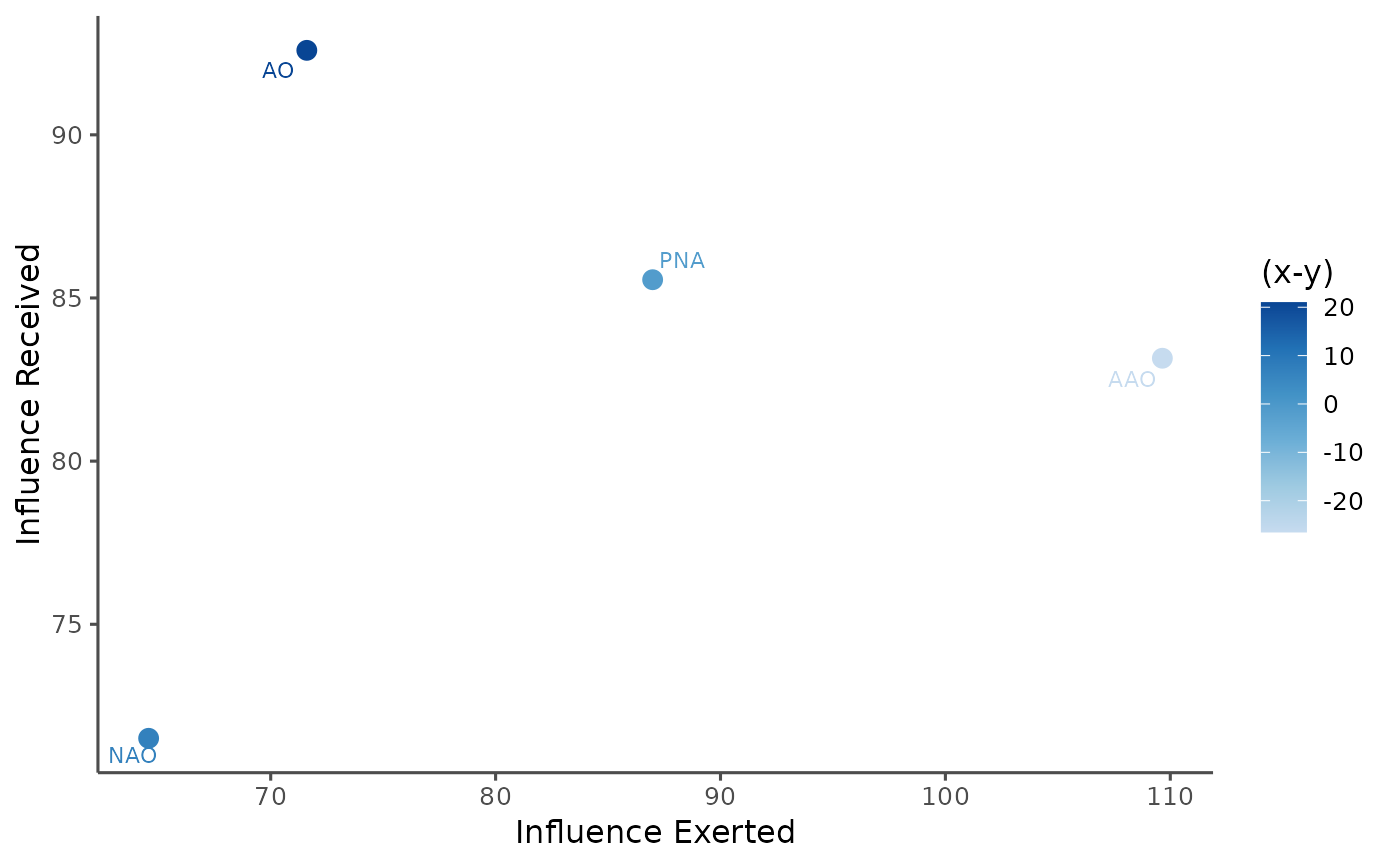
effects <- pcEffect(pcmatrix)
print(effects)
#> Pattern Causality Effect Analysis
#> --------------------------------
#>
#> Positive Causality Effects:
#> received exerted Diff
#> AO 131.66 113.90 17.76
#> AAO 111.69 140.63 -28.94
#> NAO 112.86 131.79 -18.93
#> PNA 140.90 110.80 30.11
#>
#> Negative Causality Effects:
#> received exerted Diff
#> AO 28.02 35.74 -7.73
#> AAO 44.05 33.40 10.65
#> NAO 39.64 31.94 7.71
#> PNA 27.06 37.70 -10.64
#>
#> Dark Causality Effects:
#> received exerted Diff
#> AO 140.32 150.36 -10.04
#> AAO 144.26 125.97 18.29
#> NAO 147.50 136.27 11.23
#> PNA 132.03 151.50 -19.47
#>
plot(effects)
 # }
# }