Calculate Pattern Causality Using Lightweight Algorithm
Source:R/PC.Mk.II.Lightweight.R
pcLightweight.RdImplements a computationally efficient version of the Pattern Causality Model Mk. II for analyzing causal interactions between two time series. This function uses pattern and signature spaces to assess causality through reconstructed state spaces and hashed pattern analysis.
Usage
pcLightweight(
X,
Y,
E,
tau,
h,
weighted,
metric = "euclidean",
distance_fn = NULL,
state_space_fn = NULL,
relative = TRUE,
verbose = FALSE
)Arguments
- X
A numeric vector representing the first time series
- Y
A numeric vector representing the second time series
- E
Integer; embedding dimension for state space reconstruction (E > 1)
- tau
Integer; time delay for state space reconstruction (tau > 0)
- h
Integer; prediction horizon for future projections (h >= 0)
- weighted
Logical; whether to use weighted causality strength calculations
- metric
Character string specifying the distance metric; one of "euclidean", "manhattan", or "maximum"
- distance_fn
Custom distance function for state space reconstruction
- state_space_fn
Custom function for state space transformation
- relative
Logical; if TRUE calculates relative changes ((new-old)/old), if FALSE calculates absolute changes (new-old) in signature space. Default is TRUE.
- verbose
Logical; whether to display progress information (default: FALSE)
Value
An object of class "pc_fit" containing:
total: Total causality strength (0-1)
positive: Proportion of positive causality (0-1)
negative: Proportion of negative causality (0-1)
dark: Proportion of dark causality (0-1)
Details
Calculate Pattern Causality Using Lightweight Algorithm
The function implements these key steps:
State space reconstruction using embedding parameters
Pattern and signature space transformation
Nearest neighbor analysis in reconstructed spaces
Causality strength calculation using prediction accuracy
Classification of causality types (positive/negative/dark)
See also
pcFullDetails for detailed analysis
pcMatrix for analyzing multiple time series
Examples
data(climate_indices)
X <- climate_indices$AO
Y <- climate_indices$AAO
result <- pcLightweight(X, Y, E = 3, tau = 1,
metric = "euclidean", h = 2,
weighted = TRUE, verbose = FALSE)
print(result)
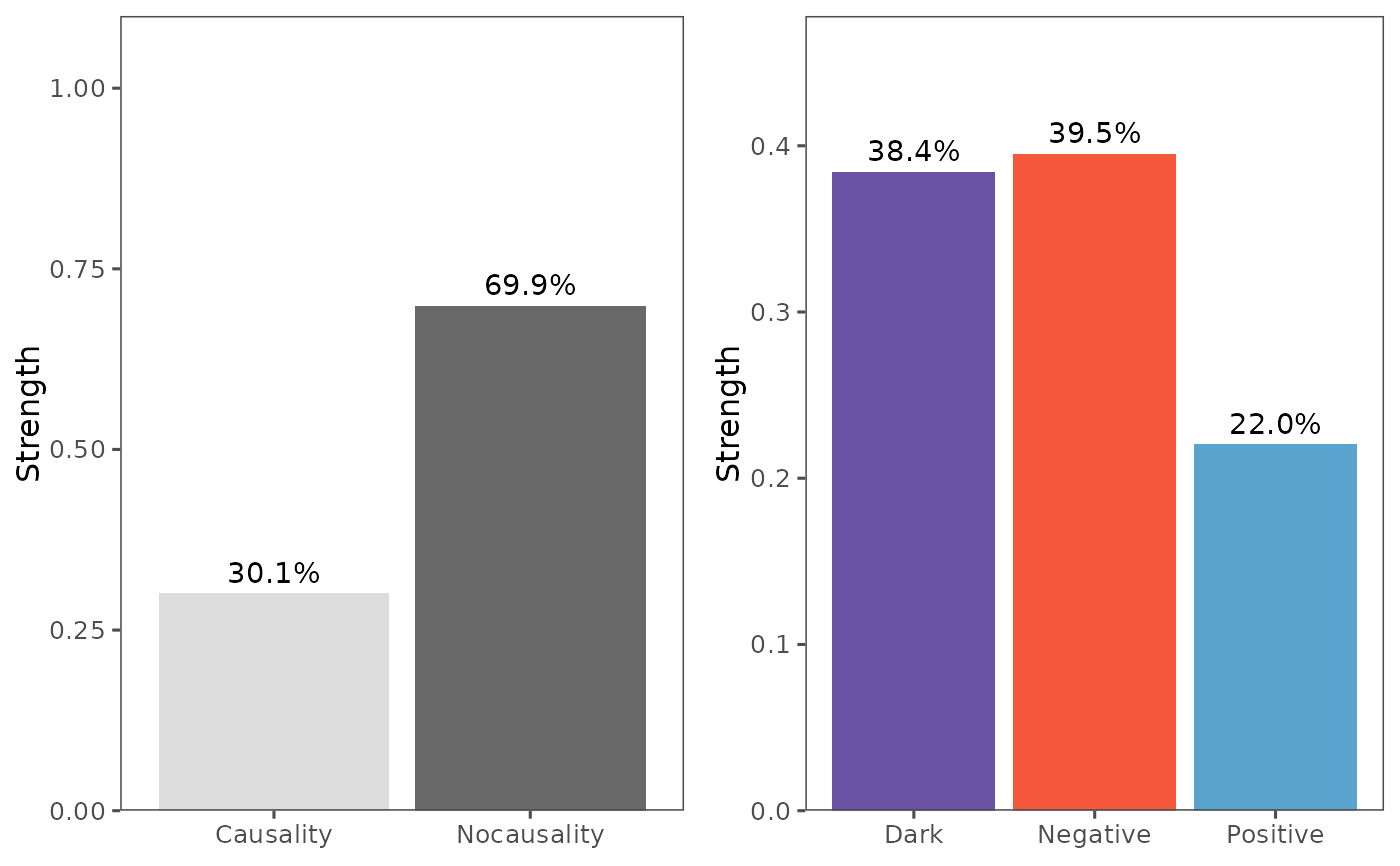
#> Pattern Causality Analysis Results:
#> Total: 0.3805
#> Positive: 0.3777
#> Negative: 0.0674
#> Dark: 0.5549
summary(result)
#> Pattern Causality Summary:
#>
#> Causality Strengths:
#> Type Value
#> 1 Total 0.38049713
#> 2 Positive 0.37770764
#> 3 Negative 0.06739703
#> 4 Dark 0.55489533
plot(result)