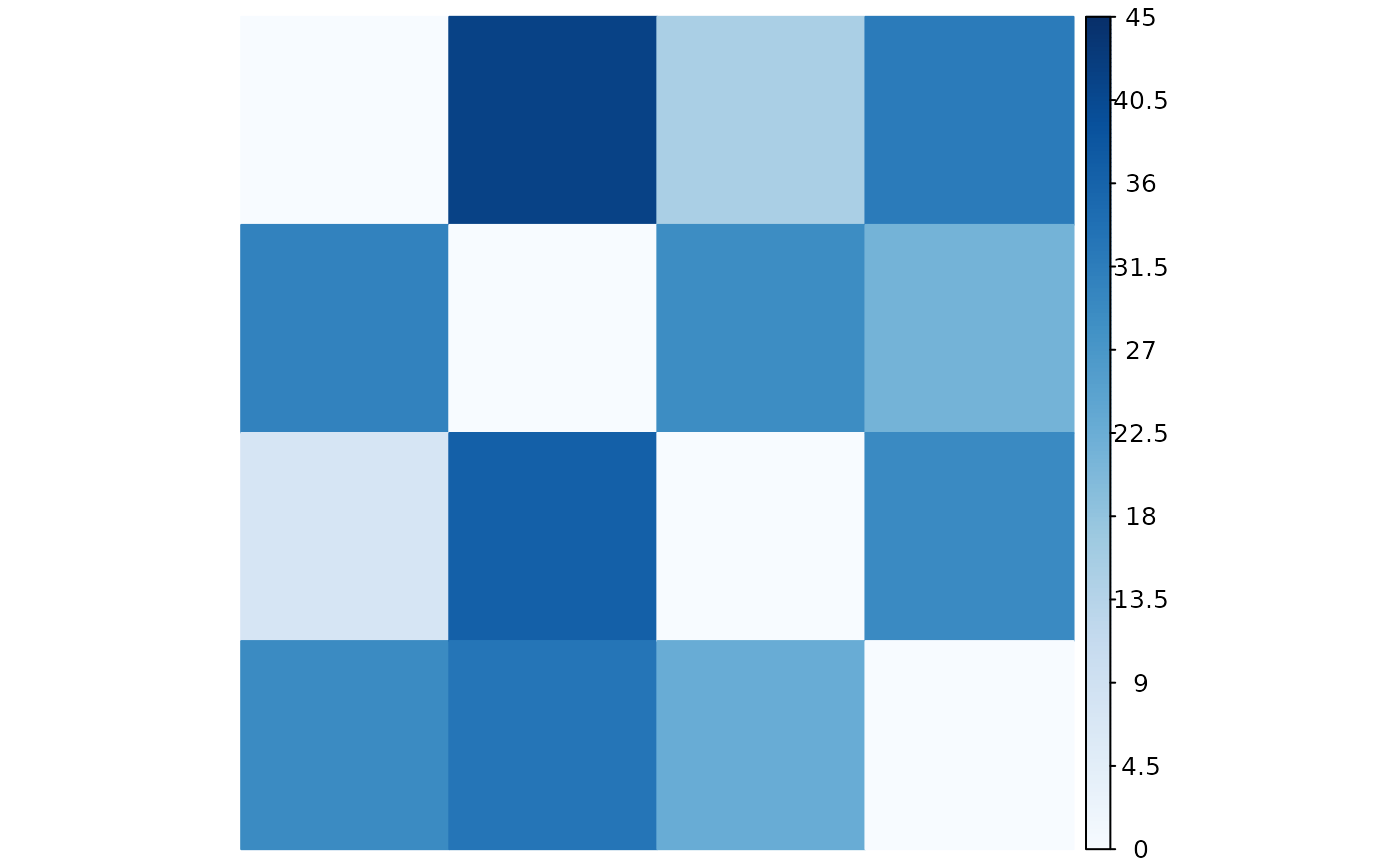
The plotMatrix function generates a visual representation of a pattern causality matrix using different methods. It allows users to visualize the positive, negative, or dark causality effects in a specified matrix, providing insight into the relationships between items.
Arguments
- pcmatrix
A list containing three matrices (
positive,negative, anddark) which represent the respective causality types for different items.- status
A character string specifying which causality matrix to plot. Must be one of
"positive","negative", or"dark".- method
A character string specifying the visualization method for the plot. Options include
"circle","square","ellipse","number","shade","color", and"pie".
Value
A visual plot of the selected causality matrix using the specified method. The plot provides a color-coded representation of the causality strengths between items.
Examples
# \donttest{
data(climate_indices)
dataset <- climate_indices[,-1]
pcmatrix <- pcMatrix(dataset, E = 3, tau = 1, metric = "euclidean", h = 1, weighted = TRUE)
#> CAUSE: AO
#> EFFECT: AO
#> EFFECT: AAO
#> EFFECT: NAO
#> EFFECT: PNA
#> CAUSE: AAO
#> EFFECT: AO
#> EFFECT: AAO
#> EFFECT: NAO
#> EFFECT: PNA
#> CAUSE: NAO
#> EFFECT: AO
#> EFFECT: AAO
#> EFFECT: NAO
#> EFFECT: PNA
#> CAUSE: PNA
#> EFFECT: AO
#> EFFECT: AAO
#> EFFECT: NAO
#> EFFECT: PNA
#> Calculation duration: 7.57771873474121
plotMatrix(pcmatrix, status = "positive", method = "color")
 # }
# }